Tutorials
0 - Introduction
1 - Hello, triangle!
2 - Hello, rectangle!
3 - Unit rectangle
4 - Scaled unit rectangle
5 - Pixel positions
6 - Default vertex shader
7 - Circle by the fragment shader
8 - Iterations and the Mandelbrot set
9 - Macros and the Julia set
10 - Using textures as output
11 - Uniforms and interactions
12 - Time marching
Draw a circle using the fragment shader
We can modify the fragment shader that we designed in the previous example to do more complex things than just coloring a gradient.
In this example, we modify the shader to draw only a circle at the center of the canvas using the default geometry and vertex shader.
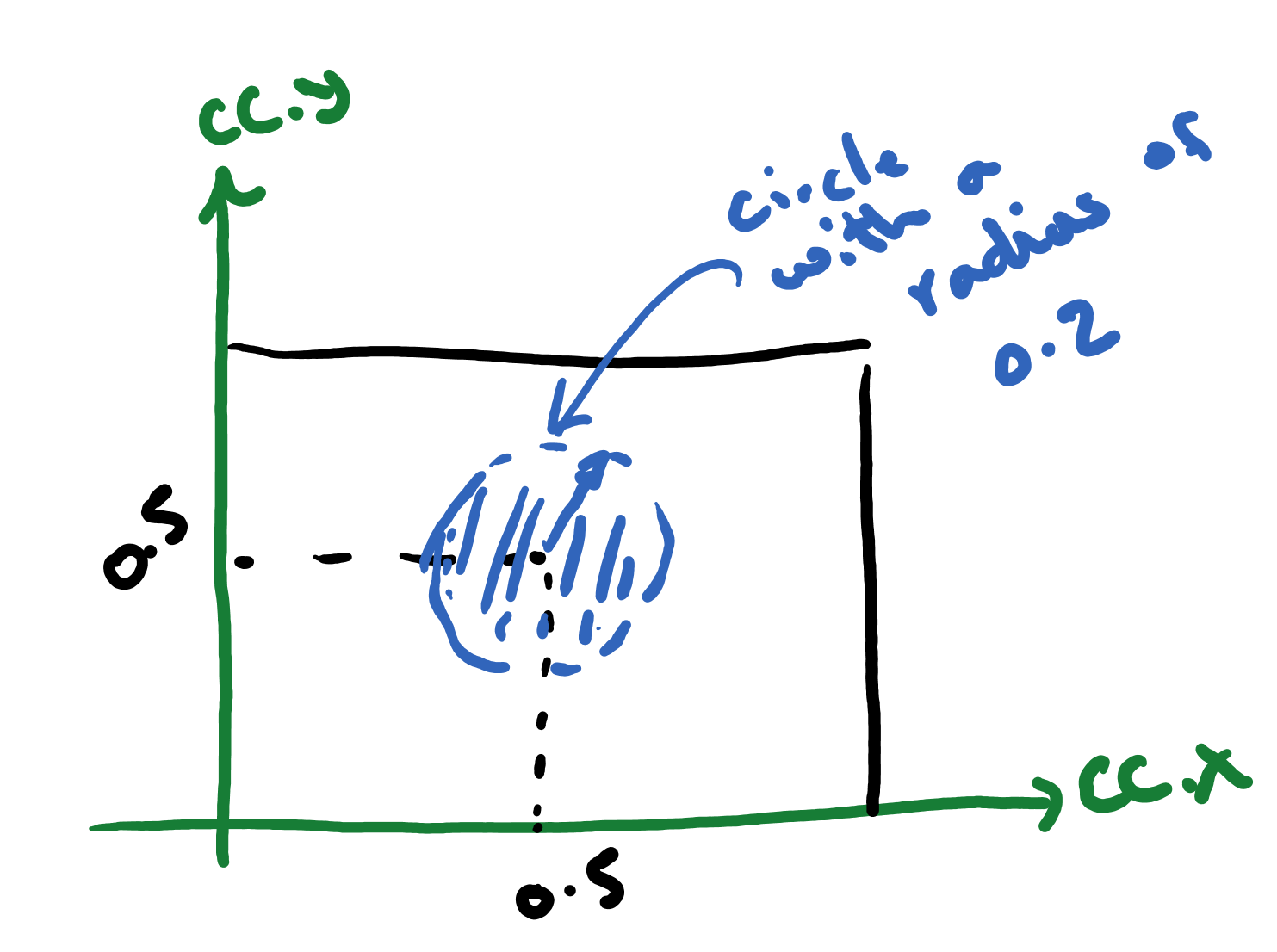
In order to do this, all we have to do is to add a conditional to our fragment shader. So, the new shader can be implemented as
#version 300 es
precision highp float ;
precision highp int ;
out vec4 outcolor ; /* output of the shader
pixel color */
in vec2 cc ; /* input from vertex shader */
// Main body of the shader
void main() {
/* Check if the pixel is inside the circle
and color it with a gradient. Otherwise, color it
black */
if ( length(cc-vec2(0.5,0.5)) < 0.2){
outcolor = vec4(cc.x,0.,0.,1.) ;
}else{
outcolor = vec4(0.,0.,0.,1.) ;
}
return ;
}
The result will be a page that produces the shape below.
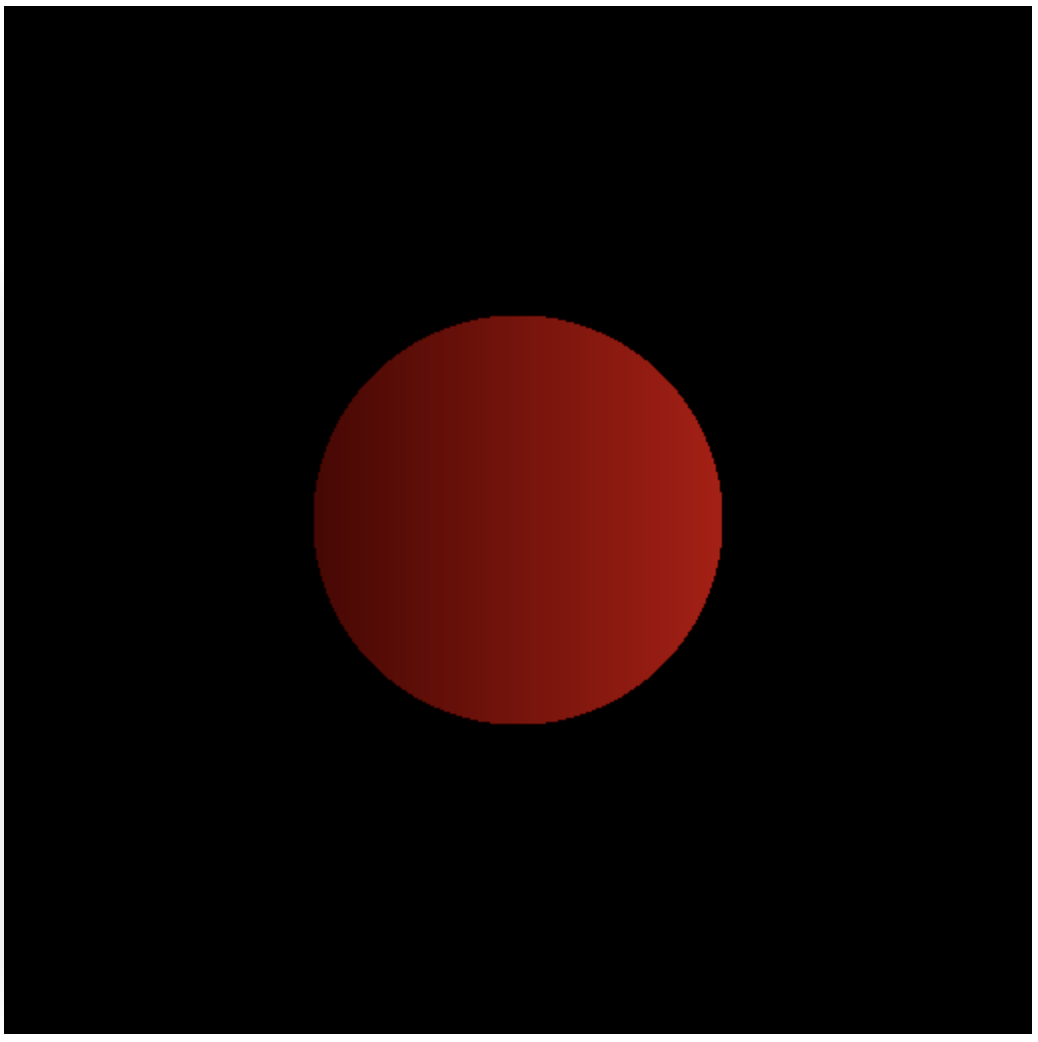
What is the geometry that is being drawn?
One would think that we are drawing a circle. However, what the WebGL 2.0 is actually drawing is just a geometry made of two triangles! The triangular surfaces are colored in the fragment shader such that you see a circle on top of them!